

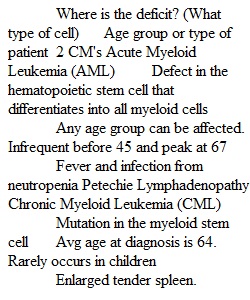
Q Week 2 Prep Assignment for Chapters 34, 35, 36 1. Fill out the table: Where is the deficit? (What type of cell) Age group or type of patient 2 CM's Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Chronic Lymphoblastic Leukemia (CLL) 2. Identify 2 differences between Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma 3. A patient tells you she must be immune to the human immunodeficiency virus because her sexual partner is HIV positive, but she is HIV negative. How would you respond? 4. What should the nurse include as essential education for the HIV patient regarding goals and benefits of antiretroviral therapy (ART)? Instructions Each week the student will complete a short preparation assignment while reading and preparing for the upcoming content. This assignment is graded for completion and timely submission per the rubric below. Student completes the assigned preparation assignment and submits in CANVAS. 10 pts Full Marks Completed the assignment and submitted it on time. 0 pts No Marks Did not complete the assignment or had a late submission 10 pts Total: 10 pts PreviousNext
View Related Questions